Case #
You have setup a point-to-site (P2S) VPN connection from your on-premises infrastructure to a VPN concentrator device, which exists on another computer room or data center or in a private or public cloud. Your P2S VPN connection may be any type of a series of available VPN types, such as OpenVPN SSL, SSTP SSL, L2TP, IKE/IPsec, etc. You either have an issue to make your VPN connection to work in the first place or you may have had a functional P2S VPN connection which for some reason has stopped working. This article provides general guidance on how to resolve P2S VPN connectivity issues.
Solution #
First off, you need to apply general network troubleshooting principles to narrow down the issue and pinpoint its root cause. You need to know if the issue occurred out of a sudden while the P2S VPN had been working for some time or whether the P2S VPN connection has never worked. Documenting the timeline of events is critical at this point, to understand which event or events may have triggered the issue. Carry out the following steps to understand the root cause and resolve the issue.
- Ask questions and perform on-site or remote audit of the environment to understand the exact network and device architecture. You need to understand what types of devices run the VPN client and what network infrastructure exists between these devices and the ISP modem.
- Re-check your P2S VPN configuration, for example in the case of Azure P2S VPN review the following KB article: https://stefanos.cloud/kb/how-to-configure-point-to-site-p2s-vpn-to-azure-vnet/. Ensure that there are no expired certificates or user credentials.
- Try to isolate the P2S VPN issue by attempting a VPN connection from another device (e.g. Windows, Linux, MacOS) in the same network and also from a different network which is totally isolated from the network in question. You can for example make use of your mobile phone's data plan (4G/5G) to check whether the P2S VPN connection gets established or not.
- If there is another routing or firewalling device between the VPN client and the ISP modem, try rebooting this device as well as the ISP modem/router and try again. Maybe any of these devices have a corruption in their RAM memory or their firmware is very old and out-of-date and needs upgrade to the latest version.
- Try to connect with a different VPN user from the same network and with a different user from their own / different network. This test is to check whether there is a global VPN server related issue or not. If at least another P2S VPN user can connect successfully from their premises, the issue lies in the specific user/connection.
- If there is another routing or firewalling device between the VPN client and the ISP modem, ensure that you review the VPN and firewall configuration of that device to verify that nothing is blocked from that device. It may be worthy checking for L2 bridge more vs L3 transparent mode configuration. Check also the Nat helpers configuration and ensure that the ALG (Application Layer Gateway) setting is set to off. Check also for potential content filtering settings which are enabled.
- Carry out a remote connection to the device(s) where the VPN client is running. Reboot these devices and try again. If issue persists, check all related Windows services running state and check the logs of the VPN client and the operating system logs for any verbose messages related to the VPN issue. Check also any anti-malware and firewall software running on the devices in question and try to temporarily disable this software and try again. Check the device's DNS and IP configuration.
If all else fails, run a network tracing tool, such as wireshark or Windows pktmon or Nirsoft network tracing utilities. For pktmon, after you run the tool in elevated mode in cmd, run the following commands to gather network traces.
pktmon filter add -p [port]
pktmon filter list
pktmon start --etw
pktmon stop
pktmon format PktMon.etl -o finaltrace.txt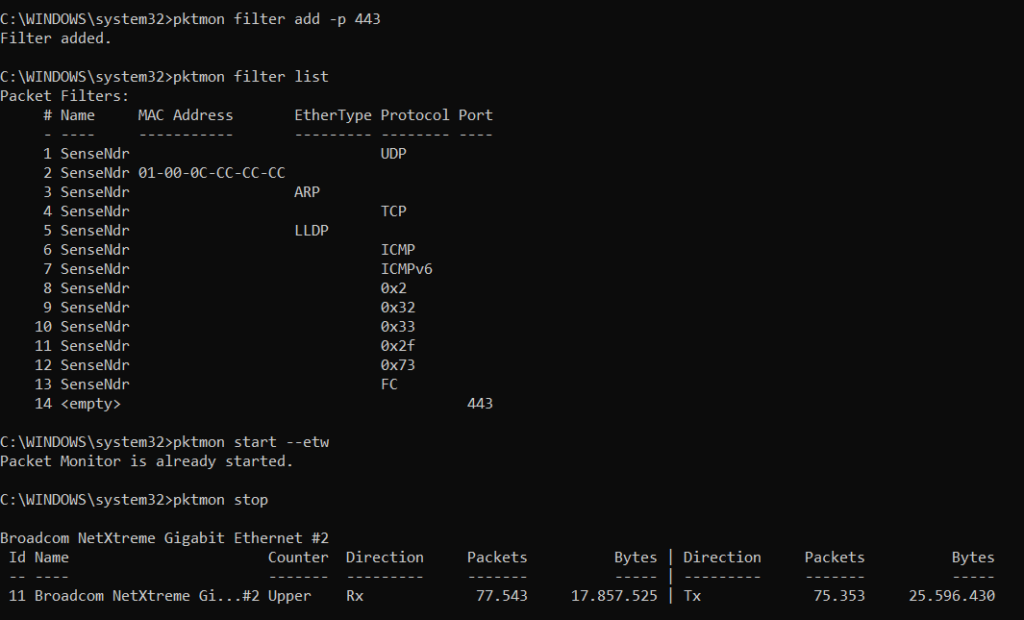
- Last but not least, call the ISP technical support team, mention the subscriber's phone line number and public IP address, provide them with all operating system and network device logs you have captured and request that they create a technical support case in order to check their ISP router, last mile and go upward in their network (for example DSLAM, ISP core network) to detect whether a firewall ACL rule exists on specific ports or IP addresses for that specific subscriber.



